- For Part 2 of this blog post containing more announcements, check out this link
- Additional Articles:
- New Service: Amazon Location
- New Service: AWS CloudShell
Its finally here! AWS re:Invent is an annual event where the fine folks at AWS lay out all the new services and enhancements they’ve been working on throughout the year.
I’m excited to say that we’ve seen some LONG awaited improvements to some core AWS services and some awesome new features.
In this blog post, I’m going to summarize all of the major announcements from Jassy’s 3 hour long keynote. If you’re looking for the full video, it unfortunately isn’t uploaded to YouTube yet, but it is available on the AWS re:Invent web portal through pre-scheduled re-broadcasts (registration required). If you’re just looking for a summary, keep on scrolling – you’ve found the right place!
I’m going to be separating out this blog post into a couple distinct sections: Compute, Data Storage, Machine Learning, and Other. If you’re interested in a particular section of announcements, feel free to skip ahead.
So lets jump right into it and go over the major product and feature announcements this year in re:invent 2020.
Compute
EC2 Announcements
Announcement #1 – New MacOS EC2 Instances!
Holy smokes, its finally happening! Jassy glossed over this announcement in the early sections of the presentation but boy oh boy is it a game changer. EC2 has long been adding to its variety of hardware – usually by adding more memory, compute, or even adding graphics/ml capabilities to new instances. This year, they anounced the the ability to launch MacOS instances, powered by Mac mini hardware and running on the AWS Nitro System.
The instances run on macOS 10.14 and 10.15 and are a welcome addition to the EC2 family. Developers no longer need to run crummy emulators or virtual machine to test their apple applications and can finally do so with native apple hardware. Woohoo! Check out this link for a detailed blog post on the announcement.
I also wanted to throw in here that Jassy also announced the d3 and d3en instance types that are well suited for big data analytics, clustered file systems, and data lakes. They offer significant performance improvements to their previous d2 generation models including 7.5x higher network speed, 7x higher storage capacity, 100% higher disk throughput, and more. Read more about it here.
Announcement #2 – New Gravitron c6gn instances
Gravitron is AWS take on building their own CPUs. Jassy himself commented that he did not expect the level of interest they have seen in this chip on their EC2 line.

In today’s keynote, Jassy announced the c6gn series of EC2 instances that deliver 100 Gbps network bandwidth, 38 Gbps EBS (Elastic Block Store Bandwidth), networking improvements, and a more attractive price/performance model. This is a huge step up from the classic c6g instances (over 4x more performance in some cases!).
C6gn instances will be available in a variety of sizes to suit your processing needs. These instances will be available likely in the second half of this month (December 2020). For more information, see this link.
Container (ECS) Announcements
Jassy started his discussion of the compute section highlighting the rapid adoption of container and serverless based compute services. AWS has been listening to your feedback and made several innovations in this space.
Announcement #3 – ECS and EKS Anywhere
ECS (Elastic Container Service) and EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) are two services in the AWS ecosystems dedicated to providing container management support. The most popular containerization product today is Docker, where developers can configure and launch their instances using an easy to design Dockerfile.
With ECS and EKS anywhere, AWS is bridging the gap between cloud based and on premise workloads. The idea of this service is to allow you to run the ECS and EKS frameworks using your own metal and in your own datacentre.
These new products solved a problem many developers can relate to, security. Now comapnies can keep their data on premise and locked down in their data center. Less sensitive workloads can always still be run in the cloud.
Serverless (Lambda) Announcements
Announcement #4 – Lambda MS Level Billing
This was a bit of a smaller announcement quickly mentioned by Jassy. Previously, Lambda billed the amount of time your invocations take by rounding up to the nearest hundredth millisecond. This means that if your invocation took < 5 ms to invoke, you would still be charged for the full 100ms duration. At first glance, this may seem negligible, but if you have enough invocations at very fast speeds, the costs can quickly get out of control.
With the new announcement, Lambda is now billing at MS level granularity. Users should notice the update in their AWS console by looking at a request ID and seeing the ‘Billed Duration’ field new reflects the exact number of milliseconds it took. Yay for more accurate billing! More details here.
Announcement #5 – Increased Lambda Memory from 2gb to 10gb
For years now, Lambda functions have been limited to 2gb of memory for invocations. This means that if you were using Lambda to run some heavy memory based workloads, your invocations could easily run out of memory.
With this announcement, Lambda dialed up the amount of available memory to up to 10gb. This change should unblock use cases that were suited for Lambda, but not viable due to memory constraints.
Keep in mind though this doesn’t come for free – Lambda invocations configured to use more memory are charged at much higher rates even if you don’t use all the memory – so be careful! More details here.
Announcement #5.5 – Containzerized Lambdas
Many aws users prefer the control over their execution environment through the user of Docker Containers. If that sounds familiar, AWS has answered your prayers.
This year, Jassy announced Container based Lambda environments. Using this new feature, users can now create and deploy containers up to 10gb in size for their lambda invocations here. I’d be a little bit wary of huge deployment images though, it could lead to the dreaded cold start problem.
For more information on this feature, read more here.
Announcement #6 – NEW SERVICE: AWS Proton
Developers have flocked to container and serverless compute options en masse. With more and more smaller components, it becomes more difficult to manage deployments. AWS Proton solves this problem and aims to streamline the deployment process for serverless and container based microservices that as a whole, are considered a single application.
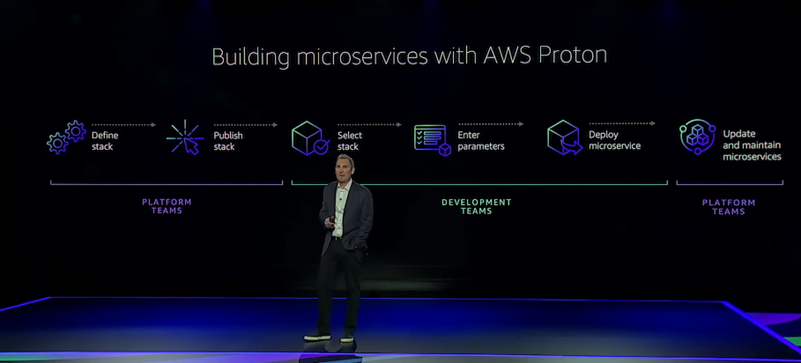
AWS Proton works by letting users define ‘Stacks’ based on templates. These stacks can be shared with other teams so you can consistently apply best practices.
Using the Proton dashboard, you can view and deploy stacks all at once, and make infrastructure upgrades as you see fit in a centralized place.
This new service is a huge deal for those of you juggling dozens of Lambda function deployments in order to get a new feature out. More details on AWS Proton can be found here.
Data Storage
Data needs are rising exponentially. The amount of data produced in a single day today, exceeds the amount generated in a single year less than two decades ago. Woah.
Announcement #7 – EBS io2 Block Express and GP3 volumes
EBS (Elastic Block Store) is an AWS service that provides detachable instance volumes that can be ported over to any instance. They are an essential component closely tied to EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud).
The EBS io2 volumes are a larger and faster ebs volume with significant gains in throughput. These units offer up to 256,000 IOPS and 4000 MBps throughput with a maximum size of 64TB.
If you’re a big EC2 user using AWS to run workloads that require ultra fast disk read/write, you’ll be happy to know the io2 block express units are available in preview. More information is available here.
Also alongside this announcement is the reveal of the gp3 volumes. These volumes are designed to be high performance and designed for use specifically with EC2 based services. The gp3 is the 7th variation of EBS volume types and comes after its predecessor, the gp2. GP3 provides consistent IOPS performance and is well suited for configurations that require conssitently high performance at low latency, such as MySQL or Postgres databases. More info on gp3 available here.
Announcement #8 – Aurora Serverless, No More Cold Start – FINALLY!!!!!!
Aurora is AWS ‘database as a service’ offering that simplifies much of the work on the developers part to create, maintain, and scale databases.
A tangential offering of Aurora was Aurora Serverless. With Aurora servless, users did not have to keep a database instance running 24/7 (and incurring significant cost), but could instead use the ‘serverless’ model that served data from your database on demand.

Sounds perfect right? Not so fast. The big problem with Aurora Serverless was that it suffered from a problem called ‘Cold Start’. Cold start means that during periods where your database has not received any traffic, it will scale down the database instance behind the scenes. This meant that whenever a database call came in after a period of low traffic, the first call could take between 5 and 50 seconds. Yuck.
In this new announcement, the cold start problem for Aurora Serverless is FINALLY solved. Users can now get subsecond, instant performance even in cases of prolonged low or zero traffic. Details regarding cost were not mentioned and I hope this comes for free, but we’ll see as more details arise. More info on Aurora is available here.
Announcement #9 – Babelfish for Aurora Postgres
This announcement appears to be a direct attack on Microsoft. Apparently earlier in the year, Microsoft was facing some flak for modifying their usage licenses to prohibit using them with cloud providers (except Azure). Not so customer focused.
Babelfish understands both the Microsoft based TSQL dialect and traditional SQL on Aurora Postgres. This new service allows users to easily migrate from SQL Server isntances to Postgres.
Babelfish provides a translation ‘shim’ layer for SQL server and allows you to switch easily between SQL Server and Postgres with no downtime.
This new service looks to kill the vendor lock in barrier Microsoft users typically face when trying to migrate to AWS.
Announcement #10 – AWS Glue Elastic Views
This announcement is probably the most underrated one of the entire Jassy Keynote. The new feature of the Glue service allows developers to ‘Project’ their database from one source into another – automatically.
Prior to this, if a developer wanted to get their database from DynamoDB into Redshift for analysis, they would have to build a datapipeline to listen to DynamoDB streams, input that data to firehose, deliver that data to s3, and then finally initiate a Redshift S3 Copy command to move that data into Redshift. This was a nightmare.
With AWS Glue Elastic Views, AWS is now taking care of this complexity for free. Now developers can ‘point and click’ their source and target databases and watch the magic migration happen. Possible sources include Aurora, RDS, and Dynamo, and Targets include Redshift, ElasticSearch, S3, DynamoDB, Aurora, and RDS.
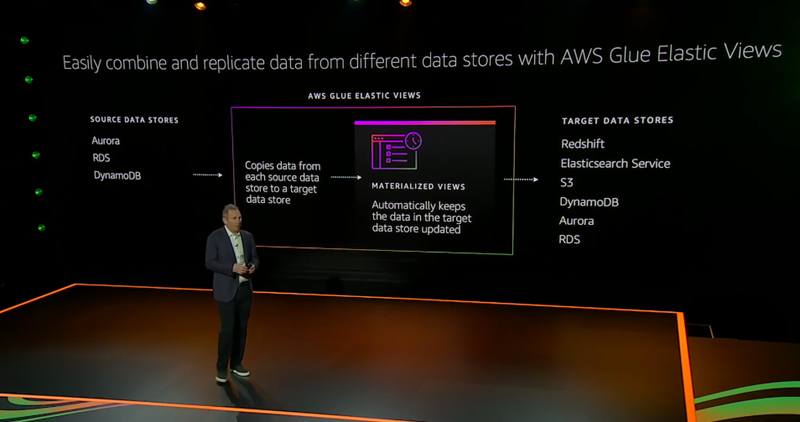
This announcement is a HUGE deal for those of you that need to synchronize databases across multiple technologies.
Machine Learning
The machine learning space saw several incremental improvements.
Announcement #11 – Sagemaker Data Wrangler
Sagemarker Data Wrangler solves the data preparation problem that comes with machine learning. Often developers need to acquire, clean, transform, and populate data into their data store before it can be consumed by Machine Learning applications.
Data Wrangler allows developers to easily point data to a data store and watch data wrangler recognize the variety of data types present in their dataset.
Whats more, developers get a UI to combine, create, preview, and apply transformations to their dataset. Ontop of this, the infrastructure required to transform your dataset is automatically provisioned and executed.
With Data Wrangler, developers no longer need to worry about the semantics of provisioning and deploying infrastructure to prepare their data, and can instead leverage AWS easy to use tools.
Announcement #12 – Sagemaker Feature Store
Machine learning models are comprised of several ‘features’ that characterize a specific aspect of your data.
Feature store acts as a repository for developers to create, store, and share features to be shared across multiple different ML based applications on AWS. Features can be made available through Sagemaker Studio for even easier access through an intuitive UI.
Announcement #13 – Sagemaker Pipelines
Sagemaker pipeline is the first exploration of Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment pipelines for Machine Learning.
It isn’t clear if this service builds ontop of AWS CodePipeline, but it sounds like its a pretty standard CI/CD tool that allows users to define workflows that comprise of steps that must succeed before progress can be made.
Either way, Sagemaker pipelines is a welcomed improvement towards faster iteration and development cycles in the ML space.
Other
Announcement #15 – NEW SERVICE: DevOps Guru
In last years re:Invent, Jassy announced Code Guru – a service meant to provide close to real-time feedback on your code to prevent bugs from getting into production.
With DevOps Guru, AWS is taking it one step further by looking to identify operational problems before they impact customers. Not only do they recognize these problems, but they actually suggest recommended actions to fix the problem – sick. This includes things like misconfigured alarms, resource limits, under provisioned capacity, overutilization, memory leaks, and much much more.
DevOps Guru uses Machine Learning models to evaluate past trends and recognize abnormalities in your resources. You can become alerted to problems through SNS notifications, Cloudwatch events, or even Slack notifications.
Announcement #16 – Quicksight Q
Quicksight is a Business Intelligence tool similar to Tableau. It allows non-technical folks to analyze and transform datasets using table and charting libraries, and through a familiar user interface.
Quicksight Q builds ontop of this feature by adding Nature Language Processing (NLP) to its repertoire of abilities. Using NLP, users can ‘free type’ queries into a search box using more natural language to retrieve data and produce insights.
For instance, you can type in something like ‘what are my most ordered products’? Any the Quicksight Q engine will know to translate this query into a SQL based query and return results. Can you say awesome?
Announcement #17 – Amazon Connect Improvements
With the covid pandemic, the need for call centre agents to work from home is larger than ever. This space has been largely ignored by technology and is ripe for re:invention. AWS significantly invested in this space and developed some new enhancements to make Call Centers even easier to build, manage, and operate.
The first announcement is Amazon Connect Wisdom. This feature aggregates data from your data store for your agents on the fly as the call is happening. Agents no longer need to fumble with multiple tools and databases to acquire relevant customer information and can instead have that information presented to them automatically.
Second comes Amazon Connect Customer Profiles. With this improvement, more context into your customers can be proactively acquired before and while a call is taking place. This means pulling up a history of past calls and aggregating all that information to your agents.
Third comes Amazon Connect Tasks. I think of this feature as Asana for call centers. It lets managers create, assign, and track tasks for their agents. They can even assign tasks based on how busy their agents are, or how much time left they have in their shift. Sweet!
Finally comes Amazon Connect Voice Id. Don’t you hate calling in somewhere and reciting your name, address, and everything else? I sure do. Connect voice ID looks to build a audio footprint of your voice so that you can be automatically identified by the agent. No more annoying questions when calling in!
Announcement #18 – Amazon Lookout
I’m not sure how I feel about this announcement, it seems very focused on those in machinery space. Amazon lookout provides anomaly detection, sound detection, vibration assessment, and temperature detection for predictive maintenance of hardware. Cool, I guess?
Summary
This year’s re:Invent is starting off with a bang. Although we’re seeing less ‘new’ services compared to last year, the improvements I’m seeing are crucial solves to some very real AWS Limitations.
Personally, I’m most excited about the increase to Lambda memory limits, Aurora Serverless Cold Start fix, and AWS Glue Elastic Views. I truly see a ton a value in these three improvements and probably require an article on each topic.
Let me know down below what you think of Jassy’s keynote. What new feature/service are you most excited for?
For Part 2 of this blog post containing more announcements, check out this link.









Thanks Daniel for compiling the list.
What a great and detailed article. Thanks for highlighting all the features and providing great context to why it matters.